Principles
Brain and Breast Imaging by TCSPC NIRS Techniques
Diffuse optical tomography (DOT), aims at the reconstruction of optical properties in highly scattering media. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) is a synonym for the same technique. Biomedical applications of DOT are based on illumination of thick tissue by NIR light, detection of diffusely transmitted or reflected light, or fluorescence of endogenous or exogenous fluorophores. Typical applications of DOT techniques are optical mammography, brain imaging, and non-invasive investigation of drug effects in small animals.
In spite of the poor spatial resolution, DOT in the NIR has the benefit that the measured absorption coefficients are related to the biochemical constitution of the tissue, such as hemoglobin concentration and blood oxygenation. When exogenous markers are used, the absorption or fluorescence delivers additional information about blood flow, blood leakage or ion concentrations.
In images obtained by continuous illumination and detection it is difficult to distinguish between the effects of scattering and absorption. The situation is much better if pulsed or modulated light is used to transilluminate the tissue and the pulse shape or the amplitude and phase of the transmitted light are recorded. The general effect of variations in the scattering and absorption on the shape of the transmitted pulses is shown in the figure below.
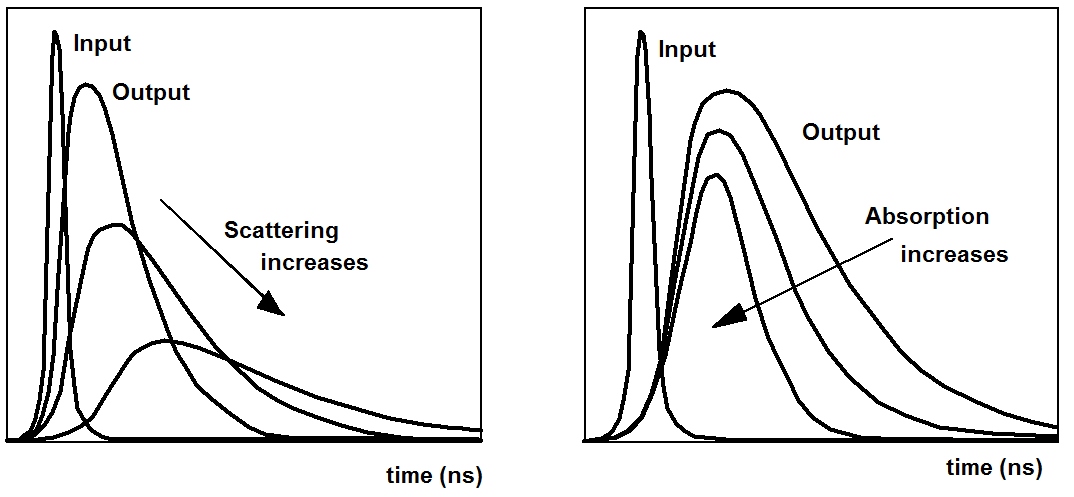
Moreover, the options of spatial reconstruction improve by using temporal resolution: Photons arriving at early times have travelled a shorter distance in the tissue than later photons. On average, they have taken a more direct path through the tissue. Temporal resolution therefore provides information on the depth in which the detected inhomogeneities are located.
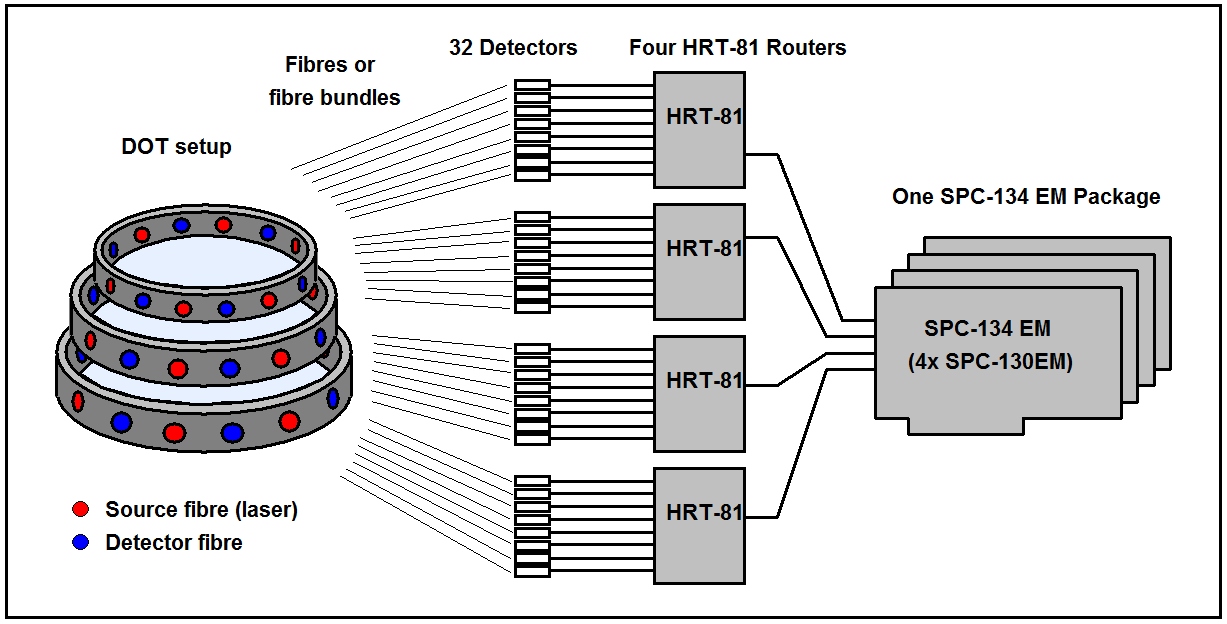
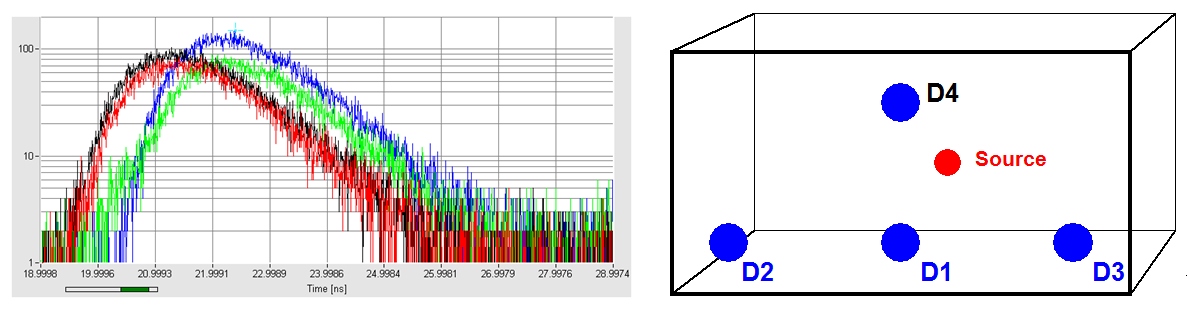
Typical clinical applications are brain imaging and breast imaging. Brain imaging is usually performed in a multi-source multi-detector setup, breast imaging in a scanning setup. The system architecture for these cases is shown in the figures below. The setups have in common that the diffusely transmitted light is recorded by several detectors for different source-detector combinations or different projection angles. In addition, several laser wavelength may be used to obtain separate data for oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin, water, or exogenous absorbers.
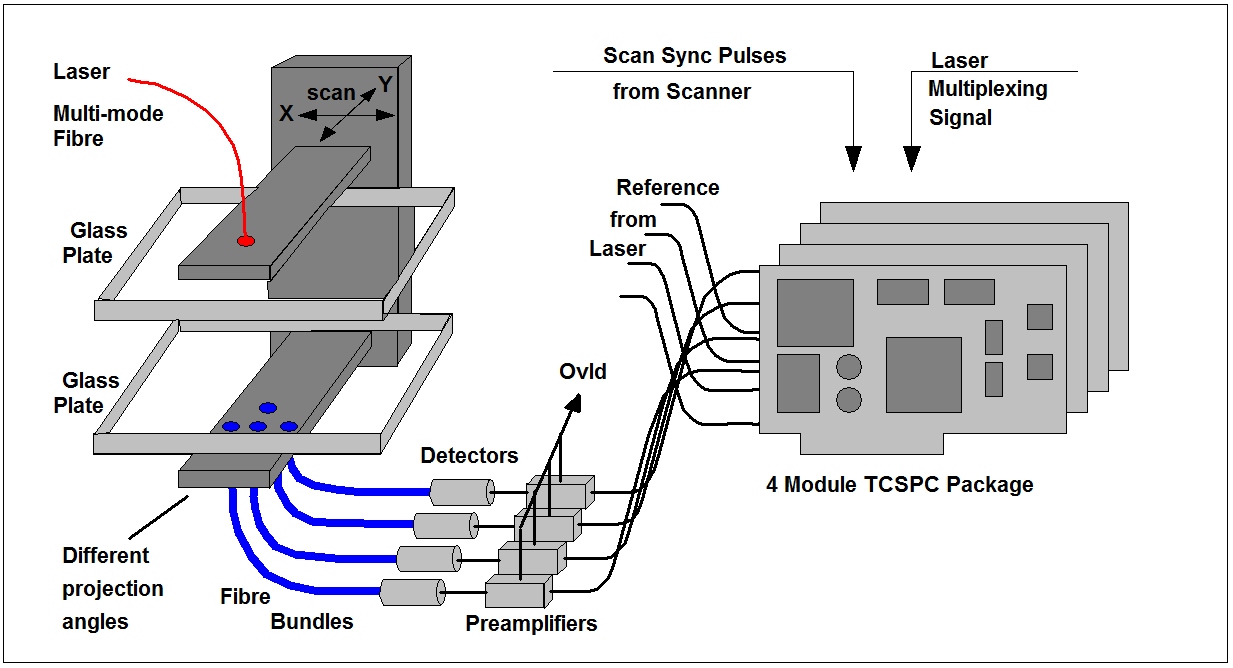
Transmitted signals (Time-of-flight distributions) from the mammography setup shown above are shown in the figure below. The curves are for the three different projection angles, as shown on the right.
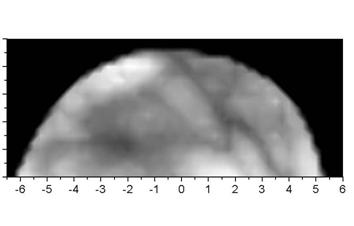
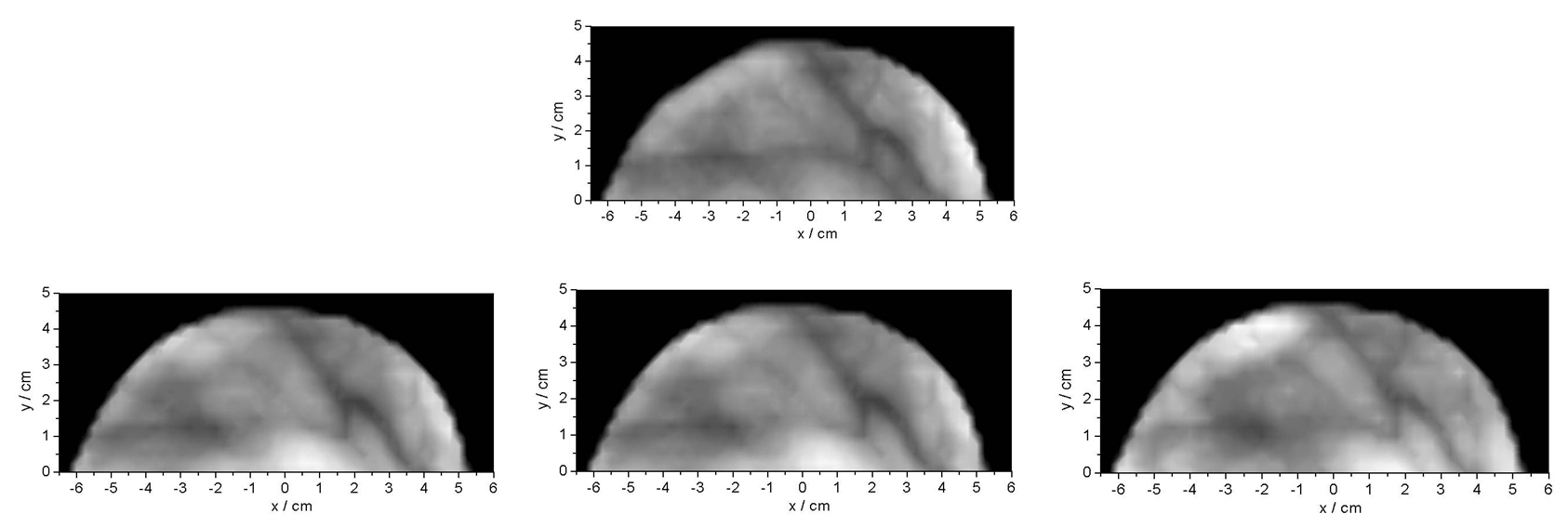
By performing an x-y scan and recording time-of-flight curves for every point of the scan images of the internal tisue can be constructed. There are different construction algorithms: Time gating, the use of moments of the time-of-flight distributions, an fit algorithms. Mammograms (of a healthy volunteer) obatimes by time gating for late photons are shown in the figure below.
For more information, related applications and references, please see:
The bh TCSPC Handbook, chapter ‘Diffuse Optical Tomography: DOT, NIRS and fNIRS’
References
References Related to NIRS
More references in W. Becker, The bh TCSPC Handbook 7ed. (2017)
- R. Arridge, M. Cope, D.T. Delpy, The theoretical basis for the determination of optical pathlengths in tissue, temporal and frequency analysis, Phys. Med Biol. 37, 1531-1560 (1992)
- R. Arridge, J.C. Hebden, M. Schweiger, F.E.W. Schmidt, M.E. Fry, E.M.C. Hillman, H. Dehghani, D.T. Delpy, A method for three-dimensional time-resolved optical tomography, International Journal for Imaging systems and Technology 11, 2-11 (2000)
- Becker, Advanced time-correlated single-photon counting techniques. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 2005
- Cubeddu, G. Biscotti, A. Pifferi, P. Taroni, A. Torricelli, M. Ferrari, V. Quaresima, Functional muscle studies by dual-wavelength, 8-channel time-resolved oximetry, Proc. SPIE 5138, 29-34 (2003)
- Cubeddu, G. M. Danesini, F. Messina, A. Pifferi, L. Spinelli, P. Taroni, A. Torricelli, Four-wavelength time-resolved optical mammograph, Proc. SPIE 4955, 203-210 (2003)
- Gao, J. Li, L. Zhang, P. Poulet, H. Zhao, Y. Yamada, Simultaneous fluorescence yield and lifetime tomography from time-resolved transmittances of small-animal-sized phantom. Appl. Opt. 49(16) 3163-3172 (2010)
- Gao, J. Li, W. Zhang, X. Yi, X. Wang, L. Zhang, Z. Zhou, H. Zhao, A CT-analogous scheme for time-domain diffuse tomography. J. of X-Ray Science and Technology 20, 91-105 (2012)
- Grosenick, H. Wabnitz, H. Rinneberg, K.T. Moesta, P.M. Schlag, Development of a time-domain optical mammograph and first in-vivo applications, Appl. Optics, 38, 2927-2943 (1999)
- Grosenick, H. Wabnitz, R. MacDonald, H. Rinneberg, J. Mucke, C. Stroszcynski, K.T. Moesta, P.M. Schlag, Determination of in vivo optical properties of breast tissue and tumors using a laser pulse mammograph, Biomedical Topical Meetings, Technical Digest, OSA, 459 (2002)
- Grosenick, K.T. Moesta, H. Wabnitz, J. Mucke, C. Stroszcynski, R. MacDonald, P.M. Schlag, H. Rinneberg, Time-domain optical mammography: initial clinical results on detection and characterization of breast tumors, Appl. Opt. 42, 3170-3186 (2003)
- Grosenick, H. Wabnitz, K.T. Moesta, J. Mucke, M. Möller, C. Stroszczynski, J. Stößel, B. Wassermann, P.M. Schlag, H. Rinneberg, Concentration and oxygen saturation of haemoglobin of 50 breast tumours determined by time-domain optical mammography, Physics in Medicine & Biology 49, 1165-1181 (2004)
- Grosenick, K. T. Moesta, M. Möller, J. Mucke, H. Wabnitz, B. Gebauer, C. Stroszczynski, B. Wassermann, P. M. Schlag, and H. Rinneberg, “Time-domain scanning optical mammography: I. Recording and assessment of mammograms of 154 patients,” Phys. Med. Biol. 50(11), 2429–2449 (2005)
- Grosenick, H. Wabnitz, K. T. Moesta, J. Mucke, P. M. Schlag, and H. Rinneberg, “Time-domain scanning optical mammography: II. Optical properties and tissue parameters of 87 carcinomas,” Phys. Med. Biol. 50(11), 2451–2468 (2005)
- Grosenick, A. Hagen, O. Steinkellner, A. Poellinger, S. Burock, P. M. Schlag, H. Rinneberg and R. Macdonald, A multichannel time-domain scanning fluorescence mammograph: Performance assessment and first in vivo results, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82, 024302 (2011)
- C. Hebden, E.W. Schmidt, M.E. Fry, M. Schweiger, E.M.C. Hillman, D.T. Delpy, Simultaneous reconstruction of absorption and scattering images by multichannel measurement of purely temporal data, Opt. Lett. 24, 534-536 (1999)
- C. Hebden, E.W. Schmidt, M.E. Fry, M. Schweiger, E.M.C. Hillman, D.T. Delpy, Simultaneous reconstruction of absorption and scattering images by multichannel measurement of purely temporal data, Opt. Lett. 24, 534-536 (1999)
- C. Hebden, H. Veenstra, H. Dehghani, E.M.C. Hillman, M. Schweiger, S.R. Arridge, D.T. Delpy, Three-dimensional time-resolved optical tomography of a conical breast phantom, Appl. Opt. 40, 3278-3287 (2001)
- C. Hebden, A. Gibson, R.M. Yusof, N. Everdell, E.M.C. Hillman, D.T. Delpy, S.R. Arridge, T. Austin, J.H. Meek, J.S. Wyatt, Three-dimensional optical tomography of the premature infant brain, Phys. Med. Biol. 47, 4155-4166 (2002)
- C.Hebden, A. Gibson, T. Austin, R.M. Yusof, N. Everdell, D.T. Delpy, S.R. Arridge, J.H. Meek, J.S. Wyatt, Imaging changes in blood volume and oxygenation in the newborn infant brain using three-dimensional optical tomography, Phys. Med. Biol. 49, 1117-1130 (2004)
- Leblond, H. Dehghani, D. Kepshire, B. W. Pogue, Early-photon fluorescence tomography: spatial resolution improvements and noise stability considerations, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 26, 1444-1457 (2009)
- Niedre, V. Ntziachristos, Comparison of fluorescence tomographic imaging in mice with early-arriving and quasi-continuous photons. Opt. lett. 35, 369-371 (2010)
- Pifferi, A. Torricelli, P. Taroni, R. Cubeddu, Reconstruction of absorber concentrations in a two-layer structure by use of multidistance time-resolved reflectance spectroscopy, Opt. Lett. 26, 1963-1965 (2001)
- Pifferi, P. Taroni, A. Torricelli, F. Messina, R. Cubeddu, Four-wavelength time-resolved optical mammography in the 680-980-nm range, Opt. Lett. 28, 1138-1140 (2003)
- Pifferi, A. Torricelli, P. Taroni, A. Bassi, E. Chikoidze, E. Gambatistelli, R. Cubeddu, Optical biopsy of bone tissue: A step toward the diagnosis of bone pathologies. J. Biomed. Opt. 9, 474-480 (2004)
- Pifferi, J. Swartling, E. Chikoidze, A. Torricelli, P. Taroni, A. Bassi, S. Andersson-Engels, R. Cubeddu, Spectroscopic time-resolved diffuse reflectance and transmittance measurements of the female breast at different interfibre distances, J. Biomed. Opt. 9, 1143-1151 (2004)
- Pifferi A, Torricelli A, Bassi A, Taroni P, Cubeddu R, Wabnitz H, Grosenick D, Möller M, Macdonald R, Swartling J, Svensson T, Andersson-Engels S, van Veen RL, Sterenborg HJ, Tualle JM, Nghiem HL, Avrillier S, Whelan M, Stamm H., Performance assessment of photon migration instruments: the MEDPHOT protocol. Appl Opt. 44(11), 2104-2114 (2005)
- Pifferi, A.o Torricelli, P. Taroni, D. Comelli, A. Bassi, R. Cubeddu, Fully automated time domain spectrometer for the absorption and scattering characterization of diffusive media. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 053103-1 to -10 (2007)
- Pifferi, A.o Torricelli, L. Spinelli, D. Contini, R. Cubeddu,1 F. Martelli, G. Zaccanti, A. Tosi, A. Dalla Mora, F. Zappa, and S.o Cova, Time-Resolved Diffuse Reflectance Using Small Source-Detector Separation and Fast Single-Photon Gating. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 138101-1 to -4 (2008)
- Quarto, A. Torricelli, L. Spinelli, A. Pifferi, R. Cubeddu and P. Taroni, Breast Monitoring by Time-Resolved Diffuse Optical Imaging. In: W. Becker (ed.) Advanced time-correlated single photon counting applications. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York (2015)
- Rinneberg, D. Grosenick, K. T. Moesta, J. Mucke, B. Gebauer, C. Stroszczynski, H. Wabnitz, M. Moeller, B. Wassermann, and P. M. Schlag, Scanning time-domain optical mammography: detection and characterization of breast tumors in vivo, Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 4(5), 483–496 (2005)
- Rinneberg, D. Grosenick, K.T. Moesta, H. Wabnitz, J. Mucke, G. Wübbeler, R. Macdonald, P. Schlag, Detection and characterization of breast tumours by time-domain scanning optical mammography. Opto-Electron. Rev. 16, 147-162 (2008)
- E.W. Schmidt, M.E. Fry, E.M.C. Hillman, J.C. Hebden, D.T. Delpy, A 32-channel time-resolved instrument for medical optical tomography, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71, 256-265 (2000)
- Taroni, G. Danesini, A. Torricelli, A. Pifferi, L. Spinelli, R. Cubeddu, Clinical trial of time-resolved scanning optical mammography at 4 wavelengths between 683 and 975 nm, J. Biomed. Opt. 9, 464-473 (2004)
- Taroni, A. Pifferi, A. Torricelli, L. Spinelli, G.M. Danesini, R. Cubeddu, Do shorter wavelength improve contrast in optical mammography?, Phys. Med. Biol. 49, 1203-1215 (2004)
- Taroni, A. Torricelli, L. Spinelli, A. Pifferi, F. Arpaia G. Danesini and R. Cubeddu, Time-resolved optical mammography between 637 and 985 nm: Clinical study on the detection and identification of breast lesions, Phys. Med. Biol. 50, 2469-2488 (2005)
- Taroni, D. Comelli, A. Farina, and A. Pifferi, A. Kienle, Time-resolved diffuse optical spectroscopy of small tissue samples. Opt. Expr. 15, 3301-3311 (2007)
- Taroni, D. Comelli, A. Pifferi, A. Torricelli, R Cubeddu, Absorption of collagen: effects on the estimate of breast composition and related diagnostic implications. J. of Biomed. Opt. 12(1) 014021-1 to -4 (2007)
- Taroni, A. Bassi, D. Comelli A. Farina, R. Cubeddu, A, Pifferi, Diffuse optical spectroscopy of breast tissue extended to 1100 nm, J. Biomed. Opt. 14(5) 1-1 to -7
- Taroni, A. Pifferi, G. Quarto, L. Spinelli, A. Torricelli, F. Abbate, A. Villa, N. Balestreri, S. Menna, E. Cassano and R. Cubeddu, Non-invasive assessment of breast cancer risk using time-resolved diffuse optical spectroscopy, J. Biomed. Opt., 15, 060501 (2010)
- Taroni, G, Quarto, A. Pifferi, F. Ieva, A.M.Paganoni, F. Abbate, N. Balestreri, S. Menna, E. Cassano, R. Cubeddu, Optical identification of subjects at high risk for developing breast cancer. J. Biomed. Opt. 18(6) 060507-1 to -3 (2013)
- Torricelli, A. Pifferi, P. Taroni, E. Giambattistelli, R. Cubeddu, In vivo optical characterization of human tissue from 610 to 1010 nm by time-resolved reflectance spectroscopy, Phys. Med. Biol. 46, 2227-2237 (2001)
- Torricelli, L. Spinelli, A. Pifferi, P. Taroni, R. Cubeddu, Use of a nonlinear perturbation approach for in vivo breast lesion characterization by multi-wavelength time-resolved optical mammography, Opt. Expr. 11, 853-867 (2003)
- Torricelli, V. Quaresima, A. Pifferi, G. Biscotti, L. Spinelli, P. Taroni, M. Ferrati, R. Cubeddu, Mapping of calf muscle oxygenation and haemoglobin content during dynamic plantrat flexion exercise by multi-channel time-resolved near-infrared spectroscopy, Phys. Med. Biol. 49, 685-699 (2004)
- Torricelli, A. Pifferi, Spinelli, R. Cubeddu, F. Martelli, S. Del Bianco, G. Zaccanti, Time-Resolved Reflectance at Null Source-Detector Separation: Improving Contrast and Resolution in Diffuse Optical Imaging. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 078101-1 to -4 (2005)
- Valim, J. Brook, M. Niedre, Experimental measurement of time-dependant photon scatter for diffuse optical tomography. J. .Biomed. Opt. 15(6), 065006-1 to -8 ( 2010)
- Wabnitz, A. Liebert, M. Möller, D. Grosenick, R. Model, H. Rinneberg, Scanning laser-pulse mammography: matching fluid and off-axis measurements. Biomedical Topical Meetings, Technical Digest, OSA 686 (2002)
- Wabnitz, D. Grosenick, M. Möller, J. Stössel, B. Wassermann, R. Macdonald, K.T. Moesta, H. Rinneberg, Scanning laser-pulse mammography: matching fluid and off-axis measurements, In OSA Biomedical Optics Topical Meetings on CD ROM (The Optical Sciety of America, Washington, DC) (2004)
- Wabnitz, M. Moeller, A. Liebert, H. Obrig, J. Steinbrink, R. Macdonald, Time-Resolved Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Imaging of the Adult Human Brain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 662 143-148 (2010)
- Wabnitz, D. R. Taubert, M. Mazurenka, O. Steinkellner, A. Jelzow, R. Macdonald, D. Milej, P. Sa-wosz, M. Kacprzak, A. Liebert, R. Cooper, J. Hebden, A. Pifferi, A. Farina, I. Bargigia, D. Contini, M. Caffini, L. Zucchelli, L. Spinelli, R. Cubeddu, A. Torricelli., Performance assessment of time-domain optical brain imagers, part 1: basic instrumental performance protocol. J. Biomed. Opt. 19(8), 086010 (2014)
- Wabnitz, A. Jelzow, M. Mazurenka, O. Steinkellner, R. Macdonald, D. Milej, N. Zolek, M. Kacprzak, P. Sawosz, R. Maniewski, A. Liebert, S. Magazov, J. Hebden, F. Martelli, P. Di Ninni, G. Zaccanti, A. Torricelli, D. Contini, R. Re, L. Zucchelli, L. Spinelli, R. Cubeddu, A. Pifferi, Performance assessment of time-domain optical brain imagers, part 2: nEUROPt protocol. J. Biomed. Opt. 19(8), 086012 (2014)
- Wabnitz, M. Mazurenka, L. Di Sieno, G. Boso, W. Becker, K. Fuchs, D. Contini, A. Dalla Mora, A. Tosi, R. Macdonald, A. Pifferi, Time-domain diffuse optical imaging of tissue by non-contact scanning. In: W. Becker (ed.) Advanced time-correlated single photon counting applications. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York (2015)
- Wabnitz, A. Liebert, M. Möller, D. Grosenick, R. Model, H. Rinneberg, Scanning laser-pulse mammography: matching fluid and off-axis measurements. Biomedical Topical Meetings, Technical Digest, OSA 686 (2002)
- Wabnitz, D. Grosenick, M. Möller, J. Stössel, B. Wassermann, R. Macdonald, K.T. Moesta, H. Rinneberg, Scanning laser-pulse mammography: matching fluid and off-axis measurements, In OSA Biomedical Optics Topical Meetings on CD ROM (The Optical Sciety of America, Washington, DC) (2004)
